Objectives
- To demonstrate the application of a Low Select (LS) override control strategy for protecting a heat exchanger tube from overheating due to excessive heating.
- To develop a MATLAB Simulink model for the LS control strategy and evaluate its performance under different process variations.
Process Information
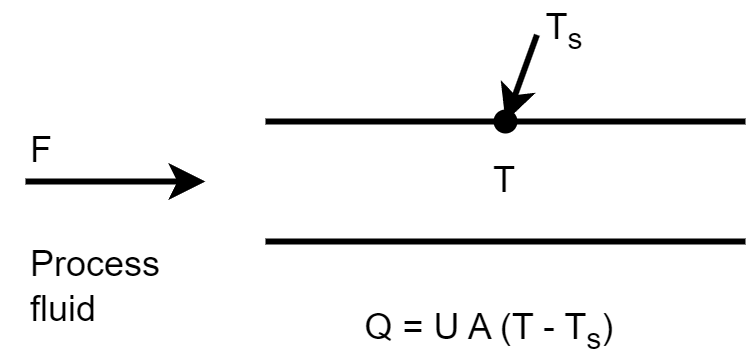
A process fluid is heated using steam in a heat exchanger.
If the process fluid flow rate suddenly increases, there will be a large drop in the process fluid temperature
However, if
Process fluid temperature transfer function
Heat exchanger tube temperature transfer function
At steady-state:
- Process fluid temperature = 300°C
- Tube skin temperature = 350°C
- Maximum allowable tube skin temperature = 400°C
Methodology
- Model Development
- Create a MATLAB Simulink model for the LS control strategy.
- Implement two controllers:
- Process fluid temperature controller
- Tube skin temperature controller
- The LS block selects the lower output to prevent overheating.
- Create a MATLAB Simulink model for the LS control strategy.
- Simulation Cases
- Nominal operation: Observe the system response to setpoint changes in process fluid temperature.
- High steam flow rate: Simulate a rapid increase in steam flow rate causing potential overheating.
- Process gain variation: Change the process gain of
- Process time constant variation: Change the time constant of
Report Format
Your report (5 pages maximum) should include the following:
- Submission Details
Include a brief table at the beginning of the report with the following information:
| Lab Title: | Lab 03 - Override Control | Student Name | ID |
| Unit: | CHEN4011 | Student 1 | 12345678 |
| Date: | 12 August 2025 | Student 2 | 87654321 |
Objective & Problem Statement
Briefly describe the LS control strategy and its purpose in preventing heat exchanger damage.
Methodology & Implementation
- Provide a Simulink diagram of the LS control strategy.
- Explain the roles of both temperature controllers.
- Describe how the LS block operates in the model.
Results
- Show the system responses for:
- Setpoint tracking
- Tube skin temperature protection under excessive heating
- Include well-labeled plots for:
- Nominal operation
- High steam flow rate disturbance
- Process gain ±10% for
- Process time constant ±10% for
- Summarize relevant performance metrics (IAE, overshoot, settling time).
- Show the system responses for:
Analysis and Discussion
Address the following:
- Under what conditions does the LS controller select the tube skin temperature controller’s output?
- How does a ±10% change in the gain of
- How does a ±10% change in the time constant of
- Quantitatively compare performance metrics between nominal and altered conditions.
Conclusion
- Summarize your findings on LS override control effectiveness.
- Discuss practical applications in industrial safety control.
Assessment Rubric (20 Marks Total)
| No | Section | Marks | Evaluation basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Objectives & Problem | 2 | Clarity of problem definition; articulation of objectives |
| 2. | Methodology and Implementation | 4 | Correctness and clarity of Simulink model; explanation of LS control strategy |
| 3. | Results | 4 | Quality, relevance, and labeling of plots; completeness of performance data |
| 4. | Analysis and Discussion | 6 | Insightful interpretation; robustness; impact of process variations |
| 5. | Conclusion and Presentation | 4 | Coherent summary; quality of writing, formatting, and visual presentation |
Citation
@online{utikar2023,
author = {Utikar, Ranjeet},
title = {Lab 03: {Override} {Control}},
date = {2023-08-13},
url = {https://amc.smilelab.dev/content/labs/lab-03/},
langid = {en}
}